 nurse : is a healthcare professional, who along with other health care professionals, is responsible for the treatment, safety, and recovery of acutely or chronically ill or injured people, health maintenance of the healthy, and treatment of life-threatening emergencies in a wide range of health care settings. ( enfermera)
nurse : is a healthcare professional, who along with other health care professionals, is responsible for the treatment, safety, and recovery of acutely or chronically ill or injured people, health maintenance of the healthy, and treatment of life-threatening emergencies in a wide range of health care settings. ( enfermera) syringe: A syringe is a simple piston pump consisting of a plunger that fits tightly in a tube. The plunger can be pulled and pushed along inside a cylindrical tube (the barrel), allowing the syringe to take in and expel a liquid or gas through an orifice at the open end of the tube. The open end of the syringe may be fitted with a hypodermic needle, a nozzle, or tubing to help direct the flow into and out of the barrel. Syringes are often used to administer injections, apply compounds such as glue or lubricant, and measure liquids. (inyectadora)
syringe: A syringe is a simple piston pump consisting of a plunger that fits tightly in a tube. The plunger can be pulled and pushed along inside a cylindrical tube (the barrel), allowing the syringe to take in and expel a liquid or gas through an orifice at the open end of the tube. The open end of the syringe may be fitted with a hypodermic needle, a nozzle, or tubing to help direct the flow into and out of the barrel. Syringes are often used to administer injections, apply compounds such as glue or lubricant, and measure liquids. (inyectadora)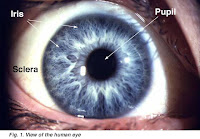 pupil: The pupil is a circular opening located in the center of the iris of the eye that controls the amount of light that enters the eye.
pupil: The pupil is a circular opening located in the center of the iris of the eye that controls the amount of light that enters the eye.It appears black because most of the light entering the pupil is absorbed by the tissues inside the eye. In optical terms, the anatomical pupil is the eye's aperture and the iris is the aperture stop. (pupila)
 sterilization: refers to any process that effectively kills or eliminates transmissible agents (such as fungi, bacteria, viruses, spore forms, etc.) from a surface, equipment, article of food or medication, or biological culture medium.Sterilization does not, however, remove prions. Sterilization can be achieved through application of heat, chemicals, irradiation, high pressure or filtration. (esterilizacion)
sterilization: refers to any process that effectively kills or eliminates transmissible agents (such as fungi, bacteria, viruses, spore forms, etc.) from a surface, equipment, article of food or medication, or biological culture medium.Sterilization does not, however, remove prions. Sterilization can be achieved through application of heat, chemicals, irradiation, high pressure or filtration. (esterilizacion) operating room: An operating room (OR), also called surgery center, is the unit of a hospital where surgical procedures are performed. An operating room may be designed and equipped to provide care to patients with a range of conditions, or it may be designed and equipped to provide specialized care to patients with specific conditions. ( quirofano).
operating room: An operating room (OR), also called surgery center, is the unit of a hospital where surgical procedures are performed. An operating room may be designed and equipped to provide care to patients with a range of conditions, or it may be designed and equipped to provide specialized care to patients with specific conditions. ( quirofano). Medical gloves: are medical safety accessories that ensure sanitary hospital conditions by limiting patients' exposure to infectious matter. They also serve to protect health professionals from disease through contact with bodily fluids.
Medical gloves: are medical safety accessories that ensure sanitary hospital conditions by limiting patients' exposure to infectious matter. They also serve to protect health professionals from disease through contact with bodily fluids.Medical gloves are traditionally made of latex and powdered with cornstarch to lubricate the gloves, making them easier to don Cornstarch replaced Lycopodium powder and/or talc but since cornstarch can also impede healing if it gets into tissues (as during surgery), non-powdered gloves are being used more often during surgery and other sensitive procedures. Special manufacturing processes are used to compensate for the lack of powder.
There are two main types of gloves: exam, and surgical. Surgical gloves have more precise sizing (numbered sizing, generally from size 5.5 to size 9), and are made to higher specifications.(guantes medicos)
 Gauze: is a thin, translucent fabric with a loose open weave. Its name may derive etymologically from the Persian word for silk, via the Spanish word "gasa". (gasa)
Gauze: is a thin, translucent fabric with a loose open weave. Its name may derive etymologically from the Persian word for silk, via the Spanish word "gasa". (gasa) Ambu bag: a flexible reservoir bag connected by tubing and a non-rebreathing valve to a face mask or endotracheal tube and used for artificial ventilation. It is self-inflating with room air or from an oxygen source. (ambu)
Ambu bag: a flexible reservoir bag connected by tubing and a non-rebreathing valve to a face mask or endotracheal tube and used for artificial ventilation. It is self-inflating with room air or from an oxygen source. (ambu) pharmacy: the place where drugs are prepared, dispensed, or sold. Also called apothecary. (farmacia)
pharmacy: the place where drugs are prepared, dispensed, or sold. Also called apothecary. (farmacia)or nares, which admit and expel air for respiration in conjunction
with the mouth. (nariz)
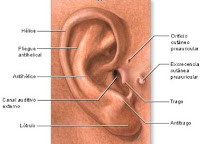 Ear: is the organ that detects sound. The vertebrate ear shows a common biology from fish to humans, with variations in structure according to order and species.The ear is part of the auditory system. (Oido)
Ear: is the organ that detects sound. The vertebrate ear shows a common biology from fish to humans, with variations in structure according to order and species.The ear is part of the auditory system. (Oido) Hands are the two intricate, prehensile, multi-fingered body parts normally located at the end of each arm of a human or other primate. (Manos)
Hands are the two intricate, prehensile, multi-fingered body parts normally located at the end of each arm of a human or other primate. (Manos) Scapula: omo, or shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone).
Scapula: omo, or shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone).The scapula forms the posterior part of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage. (Escapula)
 shoulder: joint comprises the part of the body where the humerus attaches to the scapula. The shoulder refers to the group of structures in the region of the joint. (hombro)
shoulder: joint comprises the part of the body where the humerus attaches to the scapula. The shoulder refers to the group of structures in the region of the joint. (hombro) finger: is a type of digit, an organ of manipulation and sensation found in the hands of humans and other primates. (Dedos)
finger: is a type of digit, an organ of manipulation and sensation found in the hands of humans and other primates. (Dedos) knee: joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two articulations: one between the femur and tibia, and one between the femur and patella. It is the largest and most complicated joint in the human body. The knee is a mobile trocho-ginglymus (i.e. a pivotal hinge joint), which permits flexion and extension as well as a slight medial and lateral rotation. (rodilla)
knee: joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two articulations: one between the femur and tibia, and one between the femur and patella. It is the largest and most complicated joint in the human body. The knee is a mobile trocho-ginglymus (i.e. a pivotal hinge joint), which permits flexion and extension as well as a slight medial and lateral rotation. (rodilla) leg: is a limb on a living thing's body that supports the rest of the animal above the ground between the ankle and the hip and is used for locomotion. (pierna)
leg: is a limb on a living thing's body that supports the rest of the animal above the ground between the ankle and the hip and is used for locomotion. (pierna) laboratory: is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific research experiments, and measurement may be performed. The title of laboratory is also used for certain other facilities where the processes or equipment used are similar to those in scientific laboratories. (laboratorio)
laboratory: is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific research experiments, and measurement may be performed. The title of laboratory is also used for certain other facilities where the processes or equipment used are similar to those in scientific laboratories. (laboratorio) doctor: medical practitioner, doctor of medicine, or medical doctor practices medicine and is concerned with maintaining or restoring human health through the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disease and injury . This is accomplished through a detailed knowledge of anatomy, physiology, diseases and treatment — the science of medicine — and its applied practice — the art or craft of medicine.
doctor: medical practitioner, doctor of medicine, or medical doctor practices medicine and is concerned with maintaining or restoring human health through the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disease and injury . This is accomplished through a detailed knowledge of anatomy, physiology, diseases and treatment — the science of medicine — and its applied practice — the art or craft of medicine. wheelchair: A chair mounted on large wheels for the use of a sick or disabled person. (silla de ruedas)
wheelchair: A chair mounted on large wheels for the use of a sick or disabled person. (silla de ruedas) Muscle: Muscle is the tissue of the body which primarily functions as a source of power. There are three types of muscle in the body. Muscle which is responsible for moving extremities and external areas of the body is called "skeletal muscle." Heart muscle is called "cardiac muscle." Muscle that is in the walls of arteries and bowel is called "smooth muscle." (musculo)
Muscle: Muscle is the tissue of the body which primarily functions as a source of power. There are three types of muscle in the body. Muscle which is responsible for moving extremities and external areas of the body is called "skeletal muscle." Heart muscle is called "cardiac muscle." Muscle that is in the walls of arteries and bowel is called "smooth muscle." (musculo)  Fever: refers to an elevation in body temperature. Technically, any body temperature above the normal oral measurement of 98.6 F (37 C) or the normal rectal temperature of 99 F (37.2 C) is considered to be elevated. However, these are averages, and your normal temperature may actually be 1 F (0.6 C) or more above or below the average of 98.6 F. Body temperature can also vary up to 1 F (0.6 C) throughout the day. ( fiebre)
Fever: refers to an elevation in body temperature. Technically, any body temperature above the normal oral measurement of 98.6 F (37 C) or the normal rectal temperature of 99 F (37.2 C) is considered to be elevated. However, these are averages, and your normal temperature may actually be 1 F (0.6 C) or more above or below the average of 98.6 F. Body temperature can also vary up to 1 F (0.6 C) throughout the day. ( fiebre) Artery: A vessel that carries blood high in oxygen content away from the heart to the farthest reaches of the body. Since blood in arteries is usually full of oxygen, the hemoglobin in the red blood cells is oxygenated. The resultant form of hemoglobin (oxyhemoglobin) is what makes arterial blood look bright red. (arteria)
Artery: A vessel that carries blood high in oxygen content away from the heart to the farthest reaches of the body. Since blood in arteries is usually full of oxygen, the hemoglobin in the red blood cells is oxygenated. The resultant form of hemoglobin (oxyhemoglobin) is what makes arterial blood look bright red. (arteria) pain: An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage or described in terms of such damage. (dolor)
pain: An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage or described in terms of such damage. (dolor) Virus: A microorganism smaller than a bacteria, which cannot grow or reproduce apart from a living cell. A virus invades living cells and uses their chemical machinery to keep itself alive and to replicate itself. It may reproduce with fidelity or with errors (mutations)-this ability to mutate is responsible for the ability of some viruses to change slightly in each infected person, making treatment more difficult.
Virus: A microorganism smaller than a bacteria, which cannot grow or reproduce apart from a living cell. A virus invades living cells and uses their chemical machinery to keep itself alive and to replicate itself. It may reproduce with fidelity or with errors (mutations)-this ability to mutate is responsible for the ability of some viruses to change slightly in each infected person, making treatment more difficult.  Bacteria: Single-celled microorganisms which can exist either as independent (free-living) organisms or as parasites (dependent upon another organism for life). The term bacteria was devised in the 19th century by the German botanist Ferdinand Cohn (1828-98) who based it on the Greek bakterion meaning a small rod or staff. In 1853, Cohn categorised bacteria as one of three types of microorganisms -- bacteria (short rods), bacilli (longer rods), and spirilla (spiral forms). The term bacteria was preceded in the 17th century by the microscopic animalcules described by Antony van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723).
Bacteria: Single-celled microorganisms which can exist either as independent (free-living) organisms or as parasites (dependent upon another organism for life). The term bacteria was devised in the 19th century by the German botanist Ferdinand Cohn (1828-98) who based it on the Greek bakterion meaning a small rod or staff. In 1853, Cohn categorised bacteria as one of three types of microorganisms -- bacteria (short rods), bacilli (longer rods), and spirilla (spiral forms). The term bacteria was preceded in the 17th century by the microscopic animalcules described by Antony van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723). Fungus: A single-celled or multicellular organism. Fungi can be true pathogens that cause infections in healthy persons or they can be opportunistic pathogens that cause infections in immunocompromised persons . An example of a common fungus is the yeast organism which causes thrush and diaper rash. Fungi are also used for the development of antibiotics, antitoxins, and other drugs used to control various human diseases.
Fungus: A single-celled or multicellular organism. Fungi can be true pathogens that cause infections in healthy persons or they can be opportunistic pathogens that cause infections in immunocompromised persons . An example of a common fungus is the yeast organism which causes thrush and diaper rash. Fungi are also used for the development of antibiotics, antitoxins, and other drugs used to control various human diseases.
 infection: The growth of a parasitic organism within the body. (A parasitic organism is one that lives on or in another organism and draws its nourishment therefrom.) A person with an infection has another organism (a "germ") growing within him, drawing its nourishment from the person.
infection: The growth of a parasitic organism within the body. (A parasitic organism is one that lives on or in another organism and draws its nourishment therefrom.) A person with an infection has another organism (a "germ") growing within him, drawing its nourishment from the person. The term "infection" has some exceptions. For example, the normal growth of the usual bacterial flora in the intestinal tract is not usually considered an infection. The same consideration applies to the bacteria that normally inhabit the mouth.


No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario